基于TensorFlow2实现的宠物识别系统(爬虫、模型训练和调优、模型部署)
目录
开发环境
0 项目准备
1 数据集准备
2 数据预处理
3 构建模型
4 模型训练及验证
5 模型部署
6 项目地址
开发环境
作者:嘟粥yyds
时间:2023年8月25日
集成开发工具:PyCharm Professional 2021.1
集成开发环境:Python 3.10.6
第三方库:tensorflow-gpu==2.10.0、cv2==4.7.0、gevent、functools、logging、requests、os、gradio、matplotlib、random
0 项目准备
该部分主要设置一些项目上的超参数,以便读者能根据自身情况修改这些超参数且依旧能正常运行。
IMAGE_CLASS_KEYWORD_MAP = {
'cat': '宠物猫',
'dog': '宠物狗',
'mouse': '宠物鼠',
'rabbit': '宠物兔'
}
IMAGES_ROOT = './images'
SPIDER_DOWNLOAD_PAGES = 20
SAMPLES_PER_CLASS = 305
CLASSES = ['cat', 'dog', 'mouse', 'rabbit']
CLASS_NUM = len(CLASSES)
CLASS_CODE_MAP = {
'cat': 0,
'dog': 1,
'mouse': 2,
'rabbit': 3
}
CODE_CLASS_MAP = {
0: '猫',
1: '狗',
2: '鼠',
3: '兔'
}
RANDOM_SEED = 13
TRAIN_DATASET = 0.6
DEV_DATASET = 0.2
TEST_DATASET = 0.2
BATCH_SIZE = 16
IMAGE_MEAN = [0.485, 0.456, 0.406]
IMAGE_STD = [0.299, 0.224, 0.225]
LEARNING_RATE = 0.001
TRAIN_EPOCHS = 30
MODEL_PATH = './model.h5'
'1 数据集准备
本文不使用任何公开数据集完成该任务,而是通过网络爬虫从网络上爬取需要的数据集素材,再经过人工筛选后形成最后用于训练、验证和测试的数据集。
对于爬虫而言,搜索引擎的选择十分重要。而目前搜索引擎用的比较多的无非两种——Google和百度。我分别使用Google和百度进行了图片搜索,发现百度的搜索结果远不如Google准确,于是就选择了Google,所以我的爬虫代码是基于Google编写的,运行我的爬虫代码需要你的网络能够访问Google。若你的网络不能访问Google,可以考虑自行实现基于百度的爬虫程序,逻辑都是相通的。
由于想让项目更加轻量级一些,故没有使用scrapy框架。爬虫使用requests+beautifulsoup4实现,并发使用gevent实现。
from gevent import monkey
monkey.patch_all()
import functools
import logging
import os
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
from gevent.pool import Pool
import requests
import settings
logging.basicConfig(format='%(asctime)s - %(pathname)s[line:%(lineno)d] - %(levelname)s: %(message)s',
level=logging.INFO)
keywords_map = settings.IMAGE_CLASS_KEYWORD_MAP
images_root = settings.IMAGES_ROOT
download_pages = settings.SPIDER_DOWNLOAD_PAGES
images_index_map = dict(zip(keywords_map.keys(), [0 for _ in keywords_map]))
duplication_filter = set()
headers = {
'accept-encoding': 'gzip, deflate, br',
'accept-language': 'zh-CN,zh;q=0.9',
'user-agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Linux; Android 4.0.4; Galaxy Nexus Build/IMM76B) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/46.0.2490.76 Mobile Safari/537.36',
'accept': '*/*',
'referer': 'https://www.google.com/',
'authority': 'www.google.com',
}
def try_again_while_except(max_times=3):
"""
当出现异常时,自动重试。
连续失败max_times次后放弃。
"""
def decorator(func):
@functools.wraps(func)
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
error_cnt = 0
error_msg = ''
while error_cnt < max_times:
try:
return func(*args, **kwargs)
except Exception as e:
error_msg = str(e)
error_cnt += 1
if error_msg:
logging.error(error_msg)
return wrapper
return decorator
@try_again_while_except()
def download_image(session, image_url, image_class):
"""
从给定的url中下载图片,并保存到指定路径
"""
resp = session.get(image_url, timeout=20)
if resp.status_code != 200:
raise Exception('Response Status Code {}!'.format(resp.status_code))
image_index = images_index_map.get(image_class, 0)
images_index_map[image_class] = image_index + 1
image_path = os.path.join(images_root, image_class, '{}.jpg'.format(image_index))
with open(image_path, 'wb') as f:
f.write(resp.content)
return True
@try_again_while_except()
def get_and_analysis_google_search_page(session, page, image_class, keyword):
"""
使用google进行搜索,下载搜索结果页面,解析其中的图片地址,并对有效图片进一步发起请求
"""
logging.info('Class:{} Page:{} Processing...'.format(image_class, page + 1))
downloaded_cnt = 0
params = (
('q', keyword),
('tbm', 'isch'),
('async', '_id:islrg_c,_fmt:html'),
('asearch', 'ichunklite'),
('start', str(page * 100)),
('ijn', str(page)),
)
resp = requests.get('https://www.google.com/search', params=params, timeout=20)
bsobj = BeautifulSoup(resp.content, 'lxml')
divs = bsobj.find_all('div', {'class': 'islrtb isv-r'})
for div in divs:
image_url = div.get('data-ou')
if image_url.endswith('.jpg') or image_url.endswith('.jpeg') or image_url.endswith('.png'):
if image_url not in duplication_filter:
duplication_filter.add(image_url)
flag = download_image(session, image_url, image_class)
if flag:
downloaded_cnt += 1
logging.info('Class:{} Page:{} Done. {} images downloaded.'.format(image_class, page + 1, downloaded_cnt))
def search_with_google(image_class, keyword):
"""
通过google下载数据集
"""
session = requests.session()
session.headers.update(headers)
for page in range(download_pages):
get_and_analysis_google_search_page(session, page, image_class, keyword)
def run():
if not os.path.exists(images_root):
os.mkdir(images_root)
for sub_images_dir in keywords_map.keys():
sub_path = os.path.join(images_root, sub_images_dir)
if not os.path.exists(sub_path):
os.mkdir(sub_path)
pool = Pool(len(keywords_map))
for image_class, keyword in keywords_map.items():
pool.spawn(search_with_google, image_class, keyword)
pool.join()
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()
该爬虫使用Google进行图片搜索,每个宠物搜索20页,下载其中的所有图片。当爬虫运行完成后,项目下会多出一个images文件夹,点进去有四个子文件夹,分别为cat、dog、mouse、rabbit。其中每一个子文件夹里面是对应类别的宠物图片。
其中猫图片580+张,狗图片570+张,鼠图片390+张,兔图片480+张。大约花二十多分钟时间,对爬取下来的所有图片进行筛选,剔除其中不符合要求的图片。注意,这一步是必做的,而且要认真对待。(这一步做的好可以使得最后模型的准确率提升8-10个百分点,博主亲身经历)
进行一轮筛选后,剩下图片张数:
考虑各类别样本均衡的问题,无非是过采样和欠采样。因为是图片数据,也可以使用数据增强的手段,为图片数量较少的类别生成一些图片,使样本数量均衡。但出于如下原因考虑,我直接做了欠采样,即每个类别只选取了305张样本:
使用数据增强的话,需要在原图片的基础上,重新生成一份数据集。使用数据增强后,样本数量比较多,无法同时读取到内存里面,只能写个生成器,处理哪一部分的时候,实时从硬盘读取。这个弊端还是很明显的,频繁读取硬盘会拖慢训练速度。
当然,可想而知,使用数据增强(在这里,数据增强可以作为一种过采样的方式)使数据样本都达到468,训练的效果肯定会更好,能好多少就不知道了。相较于我选择的方案复杂,读者若有兴趣可自行实现。
2 数据预处理
由于很多经典的模型接收的输入格式都为(None,224,224,3),由于我们的样本较少,不可避免地需要用到迁移学习,所以我们的数据格式与经典模型保持一致,也使用(None,224,224,3),下面是预处理过程:
import os
import random
import tensorflow as tf
import settings
samples_per_class = settings.SAMPLES_PER_CLASS
images_root = settings.IMAGES_ROOT
class_code_map = settings.CLASS_CODE_MAP
image_mean = tf.constant(settings.IMAGE_MEAN)
image_std = tf.constant(settings.IMAGE_STD)
def normalization(x):
"""
对输入图片x进行归一化,返回归一化的值
"""
return (x - image_mean) / image_std
def train_preprocess(x, y):
"""
对训练数据进行预处理。
注意,这里的参数x是图片的路径,不是图片本身;y是图片的标签值
"""
x = tf.io.read_file(x)
x = tf.image.decode_jpeg(x, channels=3)
x = tf.image.resize(x, [244, 244])
if random.choice([0, 1]):
x = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(x)
x = tf.image.random_crop(x, [224, 224, 3])
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
x = normalization(x)
y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32)
y = tf.one_hot(y, settings.CLASS_NUM)
return x, y
def dev_preprocess(x, y):
"""
对验证集和测试集进行数据预处理的方法。
和train_preprocess的主要区别在于,不进行数据增强,以保证验证结果的稳定性。
"""
x = tf.io.read_file(x)
x = tf.image.decode_jpeg(x, channels=3)
x = tf.image.resize(x, [224, 224])
x = tf.cast(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
x = normalization(x)
y = tf.cast(y, dtype=tf.int32)
y = tf.one_hot(y, settings.CLASS_NUM)
return x, y
image_path_and_labels = []
sub_images_dir_list = sorted(list(os.listdir(images_root)))
for sub_images_dir in sub_images_dir_list:
sub_path = os.path.join(images_root, sub_images_dir)
if os.path.isdir(sub_path) and sub_images_dir in settings.CLASSES:
current_label = class_code_map.get(sub_images_dir)
images = sorted(list(os.listdir(sub_path)))
random.seed(settings.RANDOM_SEED)
random.shuffle(images)
images = images[:samples_per_class]
for image_name in images:
abs_image_path = os.path.join(sub_path, image_name)
image_path_and_labels.append((abs_image_path, current_label))
total_samples = len(image_path_and_labels)
train_samples = int(total_samples * settings.TRAIN_DATASET)
dev_samples = int(total_samples * settings.DEV_DATASET)
test_samples = total_samples - train_samples - dev_samples
random.seed(settings.RANDOM_SEED)
random.shuffle(image_path_and_labels)
x_data = tf.constant([img for img, label in image_path_and_labels])
y_data = tf.constant([label for img, label in image_path_and_labels])
train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_data[:train_samples], y_data[:train_samples]))
train_db = train_db.shuffle(10000).map(train_preprocess).batch(settings.BATCH_SIZE)
dev_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(
(x_data[train_samples:train_samples + dev_samples], y_data[train_samples:train_samples + dev_samples]))
dev_db = dev_db.map(dev_preprocess).batch(settings.BATCH_SIZE)
test_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(
(x_data[train_samples + dev_samples:], y_data[train_samples + dev_samples:]))
test_db = test_db.map(dev_preprocess).batch(settings.BATCH_SIZE)
3 构建模型
数据已经全部处理完毕,该考虑模型了。首先,我们数据集太小了,直接构建自己的网络并训练,显而易见并不是一个好方案。因为这几种宠物其实挺难区分的,所以模型需要有一定复杂度,才能很好拟合这些数据,但我们的数据又太少了,最后的结果一定是过拟合,所以我们考虑从迁移学习入手。
一般认为,深度卷积神经网络的训练是对数据集特征的一步步抽取的过程,从简单的特征,到复杂的特征。训练好的模型学习到的是对图像特征的抽取方法,所以在 imagenet 数据集上训练好的模型理论上来说,也可以直接用于抽取其他图像的特征,这也是迁移学习的基础。自然,这样的效果往往没有在新数据上重新训练的效果好,但能够节省大量的训练时间,在特定情况下非常有用。而这种特定情况也包括我们面临的这一种——实际问题的数据集过小。
说到迁移学习,我最先想到的是VGG系列,就先用VGG19跑了一次。使用在 imagenet 数据集上预训练的VGG19网络,去除顶部的全连接层,冻结全部参数,使它们在接下来的训练中不会改变。然后加上自己的全连接层,最后的输出层节点为4,对应于我们的四分类问题。开始训练。
模型在训练集上的误差表现还不错,但是在验证集上的准确率基本在70+%。很明显,这个模型发生过拟合了。
于是,我盯上了DenseNet121,它的参数数量只有7M。果然,在一段时间的调优后,模型的性能有了明显的提升,训练集上达到了91%左右,验证集上的accuracy达到了93%左右。对于DenseNet121而言,这个问题已经不再是过拟合问题了,而是欠拟合了。即数据集规模过小。
import tensorflow as tf
import settings
from tensorflow.keras.utils import plot_model
def my_densenet():
"""
创建并返回一个基于densenet的Model对象
"""
densenet = tf.keras.applications.DenseNet121(include_top=False, weights='imagenet', pooling='max')
densenet.trainable = False
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Input((224, 224, 3)),
densenet,
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(),
tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(512, activation=tf.nn.relu),
tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation=tf.nn.relu),
tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization(),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(settings.CLASS_NUM, activation=tf.nn.softmax)
])
return model
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = my_densenet()
model.summary()
plot_model(model, show_shapes=True, to_file='model.png', dpi=200)
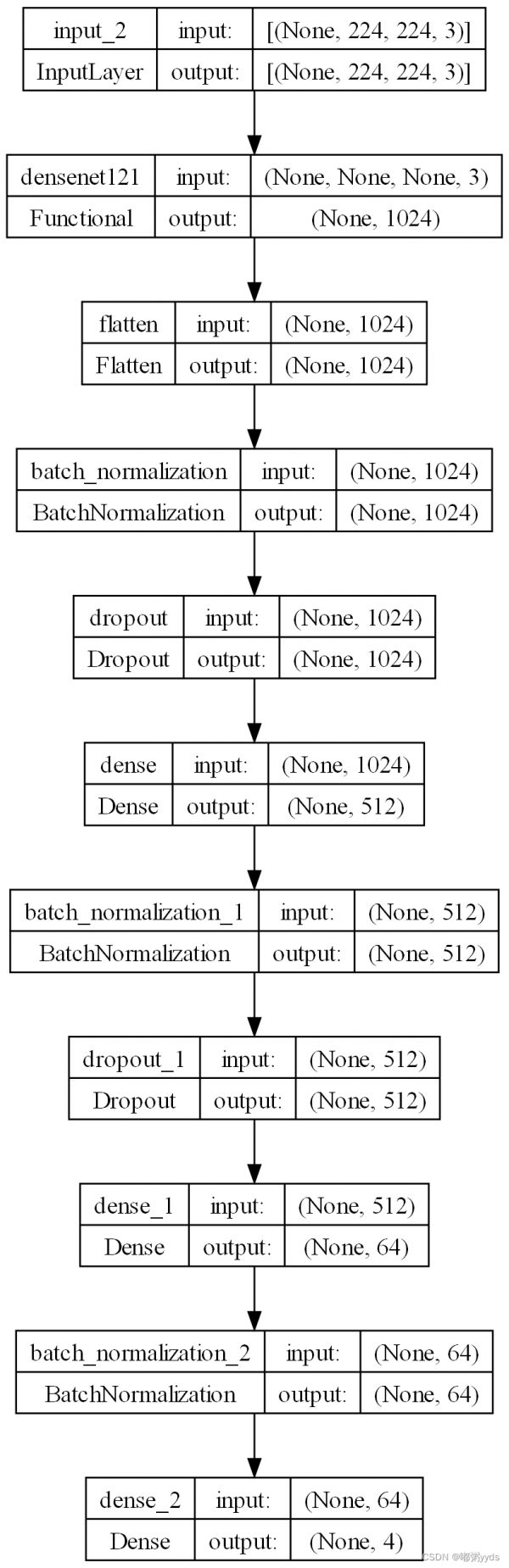 模型的summary:
模型的summary:
Model: "sequential"
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param
=================================================================
densenet121 (Functional) (None, 1024) 7037504
flatten (Flatten) (None, 1024) 0
batch_normalization (BatchN (None, 1024) 4096
ormalization)
dropout (Dropout) (None, 1024) 0
dense (Dense) (None, 512) 524800
batch_normalization_1 (Batc (None, 512) 2048
hNormalization)
dropout_1 (Dropout) (None, 512) 0
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 64) 32832
batch_normalization_2 (Batc (None, 64) 256
hNormalization)
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 4) 260
=================================================================
Total params: 7,601,796
Trainable params: 561,092
Non-trainable params: 7,040,704
_________________________________________________________________
参数总量7601796个,其中可训练参数561092个 。
4 模型训练及验证
模型和数据都已准备完毕,可以开始训练了。让我们编写一个训练用的脚本:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint, EarlyStopping, ReduceLROnPlateau, TensorBoard
from data import train_db, dev_db
import models
import settings
model = models.my_densenet()
tensorboard_callback = TensorBoard(log_dir='logs', histogram_freq=1, write_graph=True, write_images=True)
model.compile(tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(settings.LEARNING_RATE), loss=tf.keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy,
metrics=['accuracy'])
model_check_point = ModelCheckpoint(filepath=settings.MODEL_PATH, monitor='val_accuracy',
save_best_only=True)
early_stopping = EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', patience=8, restore_best_weights=True)
lr_decay = ReduceLROnPlateau(monitor='val_loss', factor=0.1, patience=3, min_lr=1e-6)
model.fit(train_db, epochs=settings.TRAIN_EPOCHS, validation_data=dev_db,
callbacks=[model_check_point, early_stopping, lr_decay, tensorboard_callback])
现在,我们可以运行脚本进行训练了,最优的参数将被保存在settings.MODEL_PATH。训练完成后,我们需要调用以下验证脚本,验证下模型在验证集和测试集上的表现:
import tensorflow as tf
from data import dev_db, test_db
from models import my_densenet
import settings
model = my_densenet()
model.load_weights(settings.MODEL_PATH)
model.compile(tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(settings.LEARNING_RATE), loss=tf.keras.losses.categorical_crossentropy,
metrics=['accuracy'])
print('dev', model.evaluate(dev_db))
print('test', model.evaluate(test_db))
for x, y in test_db:
y_pred = model(x)
y_pred = tf.argmax(y_pred, axis=1).numpy()
y_true = tf.argmax(y, axis=1).numpy()
batch_size = y_pred.shape[0]
for i in range(batch_size):
if y_pred[i] != y_true[i]:
print('{} 被错误识别成 {}!'.format(settings.CODE_CLASS_MAP[y_true[i]], settings.CODE_CLASS_MAP[y_pred[i]]))
16/16 [==============================] - 9s 99ms/step - loss: 0.1439 - accuracy: 0.9713
dev [0.1438767910003662, 0.9713114500045776]
16/16 [==============================] - 1s 85ms/step - loss: 0.1606 - accuracy: 0.9549
test [0.16057191789150238, 0.9549180269241333]
猫 被错误识别成 兔!
猫 被错误识别成 鼠!
猫 被错误识别成 狗!
鼠 被错误识别成 兔!
猫 被错误识别成 狗!
兔 被错误识别成 猫!
兔 被错误识别成 猫!
猫 被错误识别成 兔!
狗 被错误识别成 鼠!
猫 被错误识别成 兔!
狗 被错误识别成 兔!
能够看到,模型在验证集上的准确率为97.13%,在测试集上的准确率为95.49%,已经达到我的心里预期了,毕竟使用的数据确实很少。
5 模型部署
该项目的模型部署依旧是借用Gradio进行部署,其优点不言而喻——方便。
import gradio as gr
import tensorflow as tf
import settings
from models import my_densenet
import matplotlib as mpl
mpl.use('TkAgg')
model = my_densenet()
model.load_weights(settings.MODEL_PATH)
def classify_pet_image(input_image):
"""
宠物图片分类接口,上传一张图片,返回此图片上的宠物是哪种类别,概率多少
"""
x = tf.convert_to_tensor(input_image)
x = tf.image.resize(x, (224, 224))
x = x / 255.
x = (x - tf.constant(settings.IMAGE_MEAN)) / tf.constant(settings.IMAGE_STD)
x = tf.reshape(x, (1, 224, 224, 3))
y_pred = model(x)
pet_cls_code = tf.argmax(y_pred, axis=1).numpy()[0]
pet_cls_prob = float(y_pred.numpy()[0][pet_cls_code])
pet_cls_prob = '{}%'.format(int(pet_cls_prob * 100))
pet_class = settings.CODE_CLASS_MAP.get(pet_cls_code)
output_text = "宠物类别:{} n概率:{}".format(pet_class, pet_cls_prob)
return output_text
gr.close_all()
demo = gr.Interface(fn=classify_pet_image,
inputs=[gr.Image(label="Upload image")],
outputs=[gr.Textbox(label="识别结果")],
title="宠物识别Demo",
description="Classify your pet!",
allow_flagging="never"
)
demo.launch(share=True, debug=True, server_port=10055)
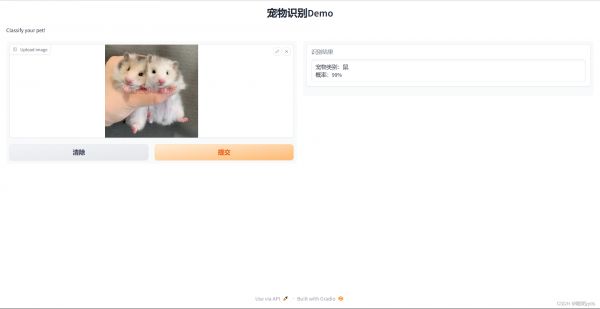
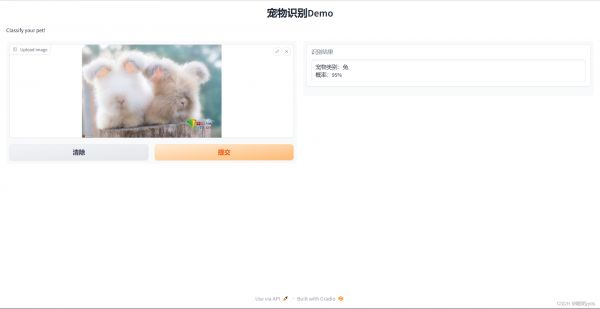
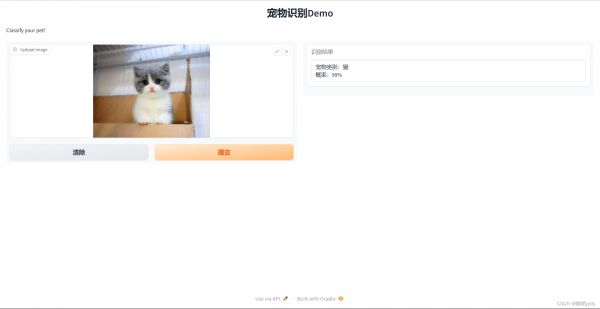
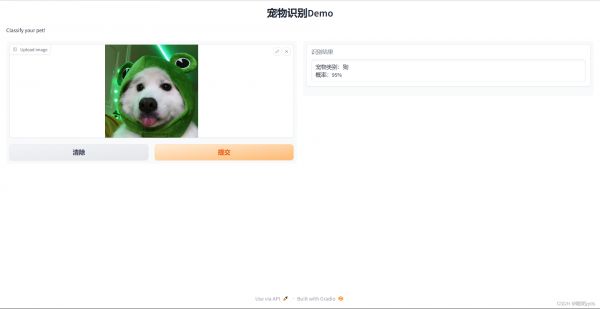
6 项目地址
Github:GitHub - 0911duzhou/OpenCV-Pet_Classifer: 基于TensorFlow2实现的宠物识别系统(爬虫、模型训练和调优、模型部署)
若无法访问Github也可在博主的主页资源里下载。
相关知识
从零开始编写一个宠物识别系统(爬虫、模型训练和调优、模型部署、Web服务)
快速部署模型和训练模型
基于卷积神经网络的宠物皮肤病识别系统,resnet50,mobilenet模型【pytorch框架+python】
基于深度学习的高精度狗狗检测识别系统(PyTorch+Pyside6+YOLOv5模型)
毕业设计:基于计算机视觉的遛狗牵绳识别系统 目标检测
PaddleSeg 自建训练集训练+评估+模型部署
毕业设计:基于深度学习的动物叫声识别系统
基于深度学习的动物识别系统(网页版+YOLOv8/v7/v6/v5代码+训练数据集)
基于深度学习的鸟类识别系统(网页版+YOLOv8/v7/v6/v5代码+训练数据集)
基于SpringBoot+Vue的宠物社交平台设计和实现(源码+LW+部署讲解)
网址: 基于TensorFlow2实现的宠物识别系统(爬虫、模型训练和调优、模型部署) https://m.mcbbbk.com/newsview390256.html
| 上一篇: 仓鼠有什么危害 |
下一篇: 心爱的“宠物鼠” |

