狗的品种识别实战(tf2.0)
在深度学习之猫VS狗中,学习了猫和狗识别的分类算法,这能很好的区分猫和狗,那如果我们想做猫的品种识别或者狗的品种识别呢?比如给一只狗的图片,我们想知道它属于斗牛犬,还是柯基,还是中华田园犬?
很容易想到,用猫狗识别的网络肯定过于简单了,因为猫和狗的特征区别较大,所以网络层次不用很深也可以实现,但是同样是狗的种类,可能有的品种之间特征区别较小,所以我们需要更深层的网络来进行特征提取。所以我感觉用resnet50可能效果会比较好,这篇文章中就使用resnet50结合vgg16来做狗的品种识别。这个模型很强大,训练才7轮,训练集的准确率就有99.27了,验证集的精确率也有66
注意:文章所用框架为tensorflow2.0,这个框架很简单,适合入门。所以建议先百度安装tensorflow2.0。
先看下自己百度找了几张图来用模型预测的结果:




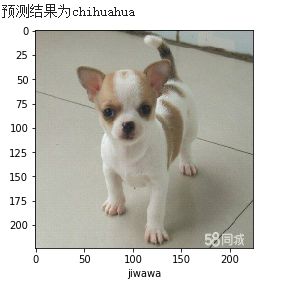
百度图片来测试,测试完了才知道二哈是个雪橇犬,哈哈哈。测试了五张图有四张正确,柴犬预测错误了。
文章的构架如下:
数据获取数据处理模型导入训练与预测完整代码1. 数据获取
文章中使用kaggle中的数据集,官方下载地址,百度云网盘下载地址,提取码:xj81 。这个数据集中有120个狗的类别。
数据集有一个训练集,一个测试集,一个训练集的csv文件,csv文件包含图片名与类别的一一对应。
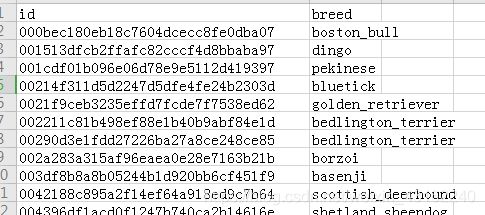
为了简单起见,文章中只用到了训练集,将训练集拆分为训练集与测试集。所以只需要下载train.zip与label.csv即可。
2.数据处理
数据的处理是最麻烦,对新手最不友好的部分,耐心看下去一定会有收获的。
获取数据列表 在tensorflow2.0中,我比较习惯将数据做成dataset,很方便导入,并且在换框架(pytorch)时,稍加改动即可使用。
先看代码,读取csv后,取训练集总数的0.9作为训练,其余的数据做验证。这里需要将label从名字改为序列号(代码中的breeds_map与train_label_list)。
import os df_train = pd.read_csv("/content/gdrive/My Drive/dogs_breeds/labels.csv") # 列举所有种类,这里的set方法可以做集合,使同一个品种只出现一次。 breeds_map = list(set(df_train['breed'])) # breeds_map = ['old_english_sheepdog', ...,'norfolk_terrier', 'silky_terrier', 'cardigan', 'otterhound'] # 生成训练集的名字列表 filename_list = df_train['id'] # 将label从名字改为序列号 label_list = [breeds_map.index(label_name) for label_name in df_train['breed']] filename_list = ['/content/gdrive/My Drive/dogs_breeds/train/train/{}.jpg'.format(x) for x in filename_list] weight_path = os.path.join("gdrive", "My Drive", "dogs_breeds", "weights")+"/"+'mymodel.ckpt' 1234567891011121314 生成dataset
先定义读数据的函数preprocess_for_train与preprocess_for_val,
然后用tensorflow的tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices生成图片名字的dataset,这里不做图片数据的dataset是为了节省内存。用map方法作用读数据的函数,用batch方法设置批量。
先看代码,其中的tf.io.read_file是读取数据,decode_jpeg是将数据转化为可用的格式,最后 /255.0是为了做归一化,这是最基础的处理,还可以给图片做增强,提高精度。
def preprocess_for_train(image_path, label): # 用tf读图,并做resize,以及归一化 image_string = tf.io.read_file(image_path) image_decoded = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_string) image_resized = tf.image.resize(image_decoded, [224, 224]) / 255.0 return image_resized, label def preprocess_for_val(image_path, label): # 用tf读图,并做resize,以及归一化 image_string = tf.io.read_file(image_path) image_decoded = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_string) image_resized = tf.image.resize(image_decoded, [224, 224]) / 255.0 return image_resized, label train_num = int(len(filename_list)*0.9) train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((filename_list[:train_num], label_list[:train_num])) tf.random.set_seed(1) # 设置随机种子,以后跑的时候固定数据的顺序 train_dataset = train_dataset.shuffle(len(filename_list[:train_num])).map(preprocess_for_train).batch(batch_size) val_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((filename_list[train_num:], label_list[train_num:])) tf.random.set_seed(2) val_dataset = val_dataset.shuffle(len(filename_list[train_num:])).map(preprocess_for_train).batch(batch_size)
123456789101112131415161718192021222324 查看数据集可以选择25个数据来查看一下我们的数据集。
# 查看25个狗狗的品种,batchsize设置越大,这里读的越慢,所以这一段可以注释掉。 for image, label in train_dataset.take(1): print(image.shape) # 若批量设置大于25的话,取这一批的前25个数据。若小于25,则设置为n*n个。 n=5 image, label = image[:n*n], label[:n*n] plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) for i in range(n*n): plt.subplot(n,n,i+1) plt.xticks([]) plt.yticks([]) plt.grid(False) plt.imshow(image[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary) plt.xlabel(breeds_map[label[i]]) plt.show() 123456789101112131415

3.模型导入
导入resnet50与vgg16 前面说了,文章中用到的模型是resnet50与vgg16,这个模型可以直接从tf导入,不用自己编写。
模型导入可以看另一篇博客。这里就不再叙述,直接调包。
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dropout, Input, concatenate, GlobalAveragePooling2D, Conv2D, BatchNormalization,MaxPooling2D, Activation, Flatten, Dense vgg16 = tf.keras.applications.vgg16.VGG16(weights='imagenet', include_top=False, input_tensor=Input( shape=(image_shape[0], image_shape[1], 3)), classes=n_class) res50 = tf.keras.applications.resnet50.ResNet50(weights='imagenet', include_top=False, input_tensor=Input( shape=(image_shape[0], image_shape[1], 3)), classes=n_class) 1234567 结合两个模型
class MyModel(tf.keras.Model): def __init__(self, n_class=2): super().__init__() self.vgg16_model = vgg16 self.res50_model = res50 self.global_pool = GlobalAveragePooling2D() self.conv_vgg = Dense(512/4, use_bias=False, kernel_initializer='uniform') self.conv_res = Dense(2048/4, use_bias=False, kernel_initializer='uniform') self.batch_normalize = BatchNormalization() self.batch_normalize_res = BatchNormalization() self.relu = Activation("relu") self.concat = concatenate self.dropout_1 = Dropout(0.3) self.conv_1 = Dense(640, use_bias=False, kernel_initializer='uniform') self.batch_normalize_1 = BatchNormalization() self.relu_1 = Activation("relu") self.dropout_2 = Dropout(0.5) self.classify = Dense(n_class, kernel_initializer='uniform', activation="softmax") def call(self, input): x_vgg16 = self.vgg16_model(input) x_vgg16 = self.global_pool(x_vgg16) x_vgg16 = self.conv_vgg(x_vgg16) x_vgg16 = self.batch_normalize(x_vgg16) x_vgg16 = self.relu(x_vgg16) x_res50 = self.res50_model(input) x_res50 = self.global_pool(x_res50) x_res50 = self.conv_res(x_res50) x_res50 = self.batch_normalize_res(x_res50) x_res50 = self.relu(x_res50) x = self.concat([x_vgg16, x_res50]) x = self.dropout_1(x) x = self.conv_1(x) x = self.batch_normalize_1(x) x = self.relu_1(x) x = self.dropout_2(x) x = self.classify(x) return x
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394.模型训练与预测
模型的训练没什么好说的,直接上代码。
模型compile过程中的loss需要特别注意,不同的loss函数对label有不同的需求,loss函数的输入为预测值与label。预测值是统一的为[0.1,0.4,0.1,0.1…]这样的概率列表,列表的长度为模型的类别数量。有的loss需要label为5这样数字(表示第6类,文章中的loss函数为这一类)。有的loss函数需要 label要为[0,1,0,0,0…](表示第2类)这样的列表。
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint model = MyModel(n_class) # 加载之前训练过的模型可以加快收敛速度,第一次训练要注释掉。 # model.load_weights(weight_path) optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=learning_rate, decay=decay_rate) # 生成checkpoint,这个是保存模型参数的工具,在fit的callbacks中调用 checkpoint_callback = ModelCheckpoint( weight_path, monitor='val_accuracy', verbose=1, save_best_only=False, save_weights_only=True, save_frequency=1) model.compile( optimizer=optimizer, loss=tf.keras.losses.sparse_categorical_crossentropy, metrics=[tf.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy()] ) model.fit(train_dataset, validation_data=val_dataset,epochs=num_epochs,callbacks=[checkpoint_callback])
1234567891011121314151617181920215.完整代码
因为我是在colab上做代码调试,所以没有做成本地的框架,若感兴趣可以自己调整一下框架。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy as np import pandas as pd import time from datetime import timedelta import math import os import scipy.misc import PIL.Image # 读csv df_train = pd.read_csv("/content/gdrive/My Drive/dogs_breeds/labels.csv") # 列举所有种类 breeds_map = list(set(df_train['breed'])) ######### 加载数据 #####读数据 filename_list = df_train['id'] # 将label从名字改为序列号 label_list = [breeds_map.index(label_name) for label_name in df_train['breed']] filename_list = ['/content/gdrive/My Drive/dogs_breeds/train/train/{}.jpg'.format(x) for x in filename_list] ##### 生成dataset def preprocess_for_train(image_path, label): # 用tf读图,并做resize,以及归一化 image_string = tf.io.read_file(image_path) image_decoded = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_string) image_resized = tf.image.resize(image_decoded, [224, 224]) / 255.0 return image_resized, label def preprocess_for_val(image_path, label): # 用tf读图,并做resize,以及归一化 image_string = tf.io.read_file(image_path) image_decoded = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_string) image_resized = tf.image.resize(image_decoded, [224, 224]) / 255.0 return image_resized, label # 生成dataset train_num = int(len(filename_list)*0.9) train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((filename_list[:train_num], label_list[:train_num])) tf.random.set_seed(1) # 设置随机种子,以后跑的时候固定数据的顺序 train_dataset = train_dataset.shuffle(len(filename_list[:train_num])).map(preprocess_for_train).batch(batch_size) val_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((filename_list[train_num:], label_list[train_num:])) tf.random.set_seed(2) val_dataset = val_dataset.shuffle(len(filename_list[train_num:])).map(preprocess_for_train).batch(batch_size) ######### 数据加载完成 ######## 配置训练参数 import os weight_path = os.path.join("gdrive", "My Drive", "dogs_breeds", "weights")+"/mymodel.ckpt" num_epochs = 10 learning_rate = 0.01 decay_rate = 1e-6 # 学习率衰减,每轮减少学习率的值 image_shape = (224, 224) batch_size=40 #一次训练多少张图,越大越快,但是对系统内存要求越高,报内存错误调低这个值,最小可以到1 n_class = len(breeds_map) print("有{}个种类".format(n_class)) ######## 配置训练参数完成 ########## 数据查看 # 查看25个狗狗的品种,batchsize设置越大,这里读的越慢,所以这一段可以注释掉。 for image, label in train_dataset.take(1): print(image.shape) # 若批量设置大于25的话,取这一批的前25个数据。若小于25,则设置为n*n个。 n=5 image, label = image[:n*n], label[:n*n] plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) for i in range(n*n): plt.subplot(n,n,i+1) plt.xticks([]) plt.yticks([]) plt.grid(False) plt.imshow(image[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary) plt.xlabel(breeds_map[label[i]]) plt.show() #########数据查看部分完成 ########模型生成部分 #### 模型导入 vgg16 = tf.keras.applications.vgg16.VGG16(weights='imagenet', include_top=False, input_tensor=Input( shape=(image_shape[0], image_shape[1], 3)), classes=n_class) res50 = tf.keras.applications.resnet50.ResNet50(weights='imagenet', include_top=False, input_tensor=Input( shape=(image_shape[0], image_shape[1], 3)), classes=n_class) #### 模型组合 class MyModel(tf.keras.Model): def __init__(self, n_class=2): super().__init__() self.vgg16_model = vgg16 self.res50_model = res50 self.global_pool = GlobalAveragePooling2D() self.conv_vgg = Dense(512/4, use_bias=False, kernel_initializer='uniform') self.conv_res = Dense(2048/4, use_bias=False, kernel_initializer='uniform') self.batch_normalize = BatchNormalization() self.batch_normalize_res = BatchNormalization() self.relu = Activation("relu") self.concat = concatenate self.dropout_1 = Dropout(0.3) self.conv_1 = Dense(640, use_bias=False, kernel_initializer='uniform') self.batch_normalize_1 = BatchNormalization() self.relu_1 = Activation("relu") self.dropout_2 = Dropout(0.3) self.classify = Dense(n_class, kernel_initializer='uniform', activation="softmax") def call(self, input): x_vgg16 = self.vgg16_model(input) x_vgg16 = self.global_pool(x_vgg16) x_vgg16 = self.conv_vgg(x_vgg16) x_vgg16 = self.batch_normalize(x_vgg16) x_vgg16 = self.relu(x_vgg16) x_res50 = self.res50_model(input) x_res50 = self.global_pool(x_res50) x_res50 = self.conv_res(x_res50) x_res50 = self.batch_normalize_res(x_res50) x_res50 = self.relu(x_res50) x = self.concat([x_vgg16, x_res50]) x = self.dropout_1(x) x = self.conv_1(x) x = self.batch_normalize_1(x) x = self.relu_1(x) x = self.dropout_2(x) x = self.classify(x) return x ########模型导入部分完成 ######### 模型训练部分 import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint model = MyModel(n_class) # 加载之前训练过的模型可以加快收敛速度,第一次训练需要注释掉 # model.load_weights(weight_path) optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=learning_rate, decay=decay_rate) checkpoint_callback = ModelCheckpoint( weight_path, monitor='val_accuracy', verbose=1, save_best_only=False, save_weights_only=True, save_frequency=1) model.compile( optimizer=optimizer, loss=tf.keras.losses.sparse_categorical_crossentropy, metrics=[tf.metrics.SparseCategoricalAccuracy()] ) model.fit(train_dataset, validation_data=val_dataset,epochs=num_epochs,callbacks=[checkpoint_callback]) ######### 模型训练完成
1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526272829303132333435363738394041424344454647484950515253545556575859606162636465666768697071727374757677787980818283848586878889909192939495969798991001011021031041051061071081091101111121131141151161171181191201211221231241251261271281291301311321331341351361371381391401411421431441451461471481491501511521531541551566.训练结果
这个模型很强大,训练才7轮,训练集的准确率就有99.27了,验证集的精确率也有66。说明模型有一点过拟合,可以减小模型参数再尝试。
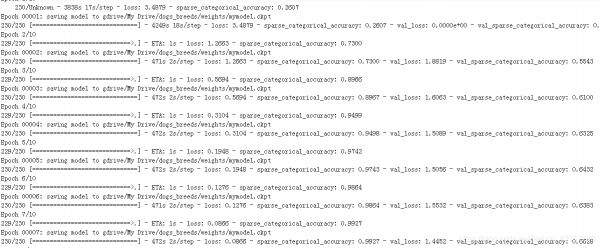
模型预测
import cv2 model.load_weights(weight_path+'mymodel_20191113.ckpt') image_path = "fadou.png" # 输入的图片路径 def preprocess_for_train(image_path): # 用tf读图,并做resize,以及归一化 image_string = tf.io.read_file(image_path) image_decoded = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image_string) image_resized = tf.image.resize(image_decoded, [224, 224]) / 255.0 image_resized = tf.expand_dims(image_resized, 0) return image_resized image = preprocess_for_train(image_path) pred = model.predict(image) pred = np.argmax(pred) y_pred = breeds_map[pred] print("预测结果为{}".format(y_pred)) plt.imshow(image[0], cmap=plt.cm.binary) plt.xlabel(image_path.split('.')[0]) plt.show()
1234567891011121314151617181920212223预测结果在文章最前面,测试图片如下:
柴犬
二哈
法斗
吉娃娃
金毛
相关知识
狗的品种识别实战(tf2.0)
实战Kaggle比赛:狗的品种识别(ImageNet Dogs)
宠物识别api接口开放:狗脸识别、猫脸识别、鼻纹识别、品种识别
原创 宠物AI识别接口全开放:狗脸识别、猫脸识别、鼻纹识别、品种识别、相似度比对
怎么知道动物的品种、如何识别宠物品种
狗鼻纹识别与猫面部识别技术分享
拍照识别犬软件有哪些 可以识别宠物品种的软件推荐
R语言深度学习玩转宠物世界:宠物识别与品种分类
抓住宠物市场红利,生产狗粮:专业指导与实战案例!
微信怎么扫描辨别狗的品种
网址: 狗的品种识别实战(tf2.0) https://m.mcbbbk.com/newsview216415.html
| 上一篇: 最新最全论文合集——基于机器学习 |
下一篇: “青少年儿童焦虑障碍”的识别和治 |

